Stay up-to date on the
latest blogs. Join our
newsletter today!
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
What Are The Leading Causes Of Laboratory Fires?

Written by Team Ryze Chemie
11 mins read · May 20, 2024

Laboratory fires are a serious threat to safety and research. They can destroy valuable equipment, halt important experiments, and endanger lives.
We understand the stress and worry these incidents cause. The fear of a fire breaking out can be overwhelming for anyone working with chemicals. But don't worry, this article is here to help.
We will look at the main causes of laboratory fires and give you practical tips to prevent them. By understanding these risks, you can make your lab a safer place for everyone.
Common Flammable Hazards in Laboratories
Laboratories are full of flammable materials. These include chemicals, solvents, gasses, and even some equipment. Recognizing these hazards is the first step in preventing fires:
Flammable liquids and their properties
Flammable liquids are liquids that can easily ignite and burn. They produce vapors that can mix with air, creating a flammable mixture. Two key properties determine a liquid's flammability: flash point and ignition temperature.
The flash point is the lowest temperature at which a liquid's vapor can ignite briefly in the presence of a spark or flame. Below the flash point, the vapor concentration is too low to sustain combustion.
Ignition temperature is the minimum temperature at which a liquid's vapor will ignite and continue burning without a constant source of ignition.
Examples of commonly used flammable liquids in laboratories
Many laboratories use various flammable liquids for experiments, analysis, and cleaning. Here are some common examples:
- Ethanol (ethyl alcohol): A clear, colorless liquid with a low flash point, commonly used as a solvent, disinfectant, and fuel.
- Acetone: A colorless liquid with a pungent odor, used as a solvent, cleaner, and nail polish remover.
- Methanol (methyl alcohol): A clear, colorless liquid with a low flash point, used as a solvent, antifreeze, and fuel.
- Isopropanol (isopropyl alcohol): A clear, colorless liquid with a rubbing alcohol scent, used as a solvent, disinfectant, and cleaning agent.
- Toluene: A colorless liquid with a strong odor, used as a solvent, paint thinner, and adhesive.
- Hexane: A colorless liquid with a gasoline-like odor used as a nonpolar solvent in organic chemistry.
Flammable gasses and their hazards
While liquids dominate laboratory flammability concerns, flammable gasses also pose a serious threat. These gasses readily form explosive mixtures with air. Common flammable gasses in laboratories include:
- Hydrogen: The lightest element, highly flammable, and can ignite with minimal spark energy.
- Methane: The main component of natural gas. It is flammable and can form explosive mixtures when leaks accumulate in confined spaces.
- Propane: A colorless gas used in Bunsen burners, highly flammable and can explode if a leak ignites near an open flame.
- Acetylene: A colorless gas used for welding and metal cutting. It is highly flammable and can decompose explosively under pressure.
Next, we will examine the leading causes of laboratory fires to help you understand how they start.
Leading Causes of Laboratory Fires
Laboratory fires can be devastating, causing injuries, property damage, and disrupting research. Fortunately, many laboratory fires are preventable by understanding the leading causes and following safe practices:
1) Flammable Liquids and Vapors
Flammable liquids and their vapors are a major fire hazard in laboratories. Here's how to minimize risks:
Spills Happen, But Minimize Them:
- Use secondary containment trays to catch spills.
- Close containers promptly and securely after use.
- Funnels can help prevent spills during transfers.
Safe Storage is Key:
- Flammable liquids belong in approved flammable cabinets.
- Store them away from heat sources and direct sunlight.
- Segregate incompatible chemicals.
- Clearly label all containers.
Vapors Travel Farther Than You Think:
- Flammable liquids give off vapors that can easily ignite from sparks or open flames, even at a distance.
- Understand the concept of flash point - the temperature at which a liquid releases enough vapor to ignite.
- Flammable vapor zones can extend several feet from a container.
- To protect yourself, always work in a fume hood with proper ventilation when using flammable liquids.
2) Electrical Malfunctions
Faulty electrical equipment is another fire risk. Here's how to stay safe:
Preventative Maintenance is Essential:
- Regularly inspect electrical cords and equipment for damage.
- Report any issues to maintenance personnel immediately.
- Don't overload circuits. Use outlets with the appropriate amperage rating for your equipment.
Use Equipment Properly:
- Never use damaged electrical cords.
- Don't modify plugs or outlets.
- Unplug equipment when not in use.
3) Improper Heat Sources
Bunsen burners and hot plates are necessary tools, but misuse can lead to fires. Here's how to use them safely:
Never Leave Heat Sources Unattended:
- Always be present when using a heat source.
- If you must step away, turn it off completely.
Control and Monitor Heat Sources:
- Use the appropriate heat setting for your experiment.
- Don't place flammable materials too close to the heat source.
Safe Shut Down is Crucial:
- Turn off heat sources completely when finished.
- Allow them to cool before storing them.
4) Uncontrolled Reactions
Some chemical reactions release heat (exothermic reactions). If not managed properly, they can ignite surrounding materials. Here's how to minimize risks:
Plan Ahead, Stay Safe:
- Before starting any experiment, thoroughly review the procedure and identify potential hazards.
- Conduct a risk assessment to determine the appropriate safety measures.
Follow Safety Protocols:
- Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) for the chemicals you are handling.
- Work in a well-ventilated area, especially when using reactive chemicals.
- Know the proper disposal methods for waste products.
By following these guidelines and staying vigilant, you can significantly reduce the risk of laboratory fires. Remember, safety is paramount in the lab.
Taking these precautions protects yourself, your colleagues, and your valuable research. But what else can contribute to laboratory fires? Let’s find out more in the next section.
Additional Contributing Factors of Laboratory Fires
Aside from the main causes, there are several additional factors that can significantly increase the risk of fire. Let's take a closer look at some key areas where vigilance can prevent disaster:
1) Poor housekeeping and cluttered laboratory benches with flammable materials
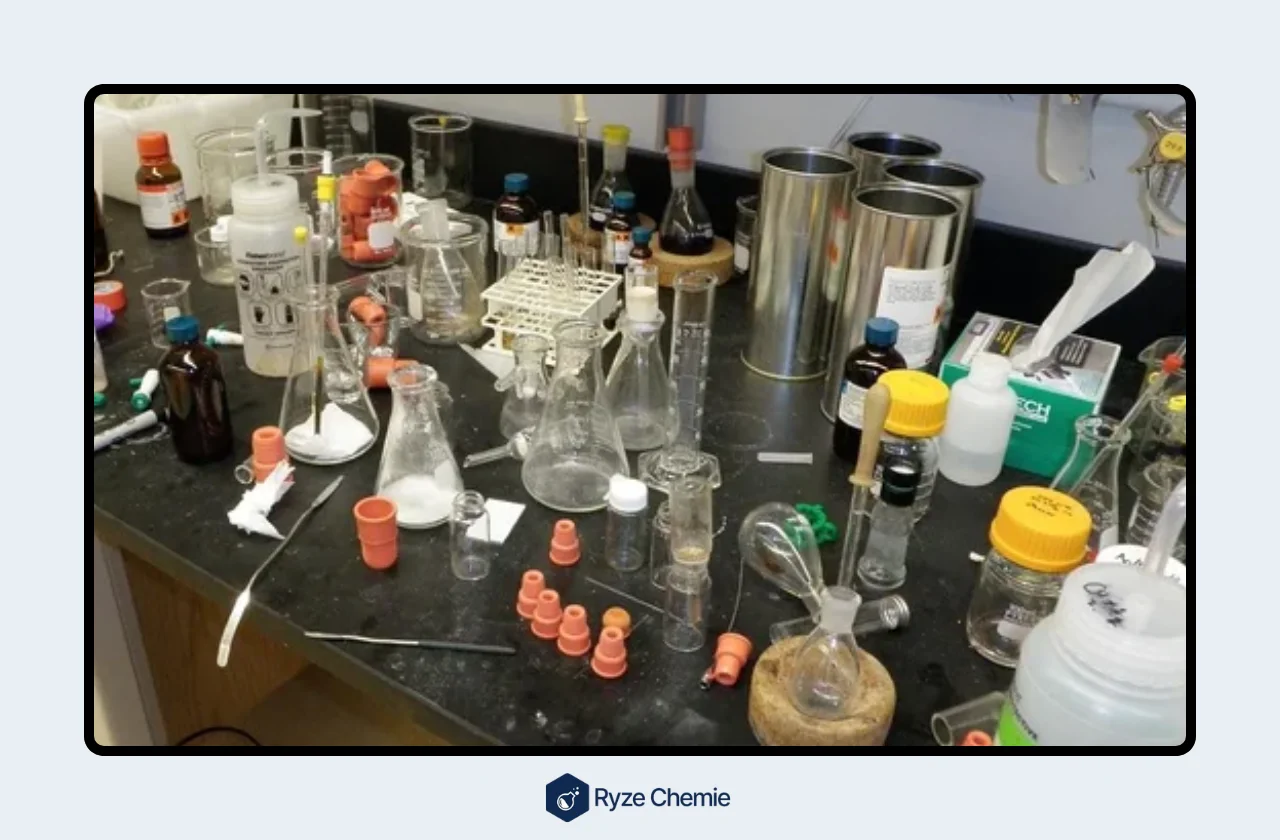

A messy lab bench is a recipe for trouble. Flammable liquids and chemicals, when left out in the open, create a fire hazard. Here's how poor housekeeping can contribute to fires:
- Accidental spills: Bumpy surfaces and cluttered areas make it easier to knock over containers, leading to spills of flammable liquids. Even small spills can quickly turn into a fire hazard if they come into contact with an ignition source.
- Blocked exits: Clutter can obstruct walkways and emergency exits. In the event of a fire, blocked exits can hinder safe evacuation and make it difficult for first responders to access the area.
- Hidden hazards: Flammable materials hidden under clutter can go unnoticed, increasing the risk of accidental ignition.
Action steps:
- Clean up spills immediately.
- Maintain clear and organized work areas.
- Store flammable liquids in designated safety cabinets away from heat sources.
- Dispose of waste properly.
2) Improper waste disposal of flammable liquids and chemicals
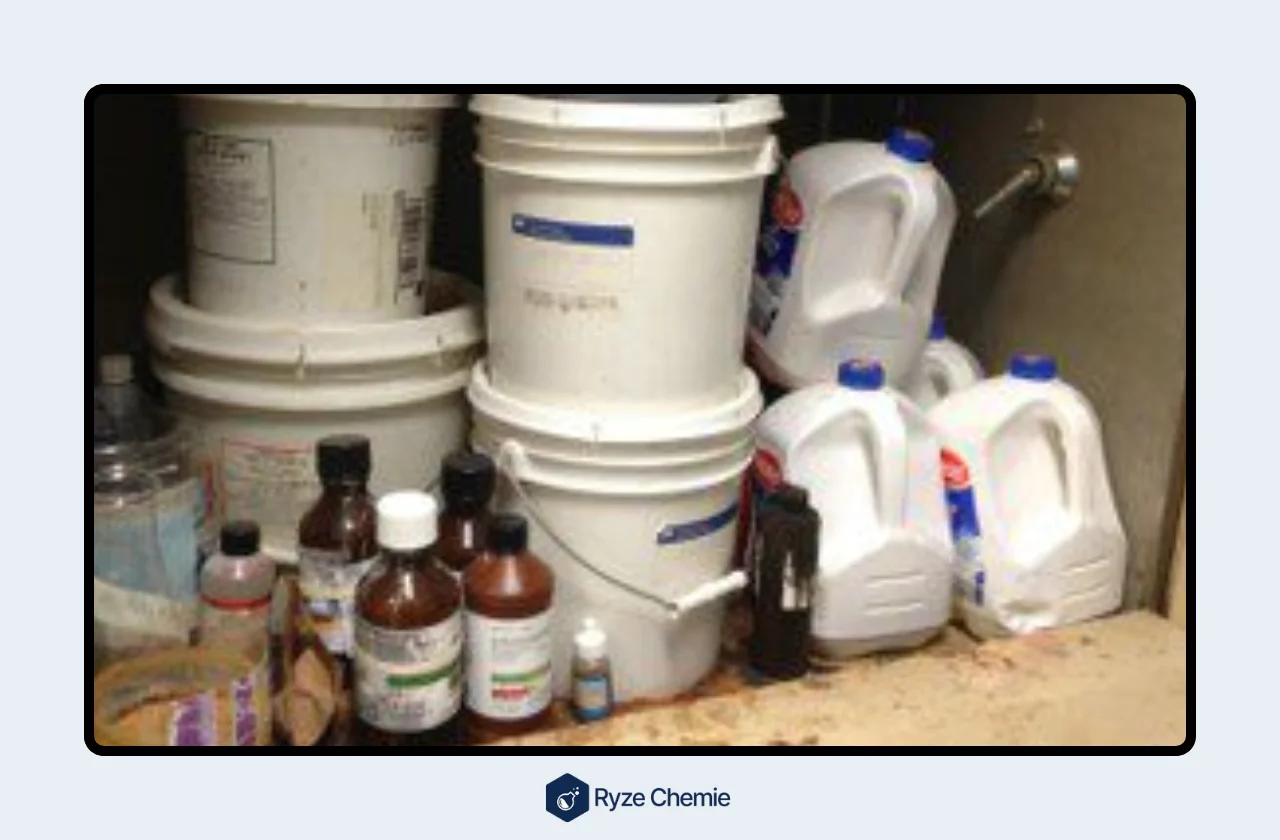

Improper waste disposal of flammable liquids and chemicals creates a significant fire risk. Here's why:
- Improper containers: Flammable waste should never be stored in flimsy or unlabeled containers. This can lead to leaks and spills.
- Mixing incompatible chemicals: Certain chemicals can react violently when mixed together. Improper disposal practices can increase the risk of such hazardous reactions.
- Full waste containers: Flammable waste containers have a designated capacity limit. Overfilling these containers can lead to spills and pose a fire hazard.
Action steps:
- Always use properly labeled containers for flammable waste.
- Familiarize yourself with the compatibility of different chemicals before disposal.
- Never mix incompatible chemicals in waste containers.
- Dispose of waste promptly. Don't let flammable waste accumulate.
- Follow your lab's specific waste disposal protocols.
3) Lack of proper training and knowledge of safety protocols

Knowledge is power, especially when it comes to laboratory safety. Here's how a lack of training can contribute to fires:
- Unfamiliarity with chemical hazards: Without proper training, researchers may not be aware of the specific fire risks associated with the chemicals they are working with.
- Incorrect handling procedures: Improper handling of flammable materials can easily lead to spills, fires, and explosions.
- Unfamiliarity with safety equipment: Fire extinguishers and other safety equipment are only effective if personnel know how to use them properly.
Action steps:
- Complete all mandatory lab safety training programs.
- Stay updated on new safety protocols and procedures.
- Never hesitate to ask questions if you are unsure about a specific chemical or procedure.
- Actively participate in lab safety discussions and training sessions.
With these contributing factors in mind, let's explore the measures you can take to prevent laboratory fires.
Measures To Prevent Laboratory Fires
Laboratory fires are a serious safety concern. They can cause injury, damage property, and disrupt valuable research. By following these simple steps, you can significantly reduce the risk of fire in your lab:
1) Following Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for handling chemicals
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are detailed instructions for working with specific chemicals or performing experiments. They outline the safest way to handle materials, use equipment, and dispose of waste. Here's why SOPs are crucial for fire prevention:
- Clear instructions: SOPs clearly explain the steps involved in an experiment, minimizing confusion and the risk of mistakes that could lead to a fire.
- Hazard identification: SOPs identify the specific hazards associated with the chemicals being used, allowing you to take appropriate precautions.
- Safe handling practices: SOPs outline safe handling practices for flammable liquids, open flames, and other potential fire hazards.
Always follow the SOPs for the experiment you are conducting. If you are unsure about any step, ask your supervisor for clarification.
2) Utilizing personal protective equipment (PPE) like safety glasses, gloves, and lab coats
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is your first line of defense against chemical splashes and burns, which can ignite flammable materials and start fires. Here's how PPE helps prevent fires:
- Safety glasses: Protect your eyes from splashes and flying debris that could ignite flammable liquids or cause sparks.
- Gloves: Shield your hands from contact with flammable chemicals that could ignite on your skin.
- Lab coats: Provide a barrier between your clothes and flammable materials, preventing them from catching fire.
Wear the appropriate PPE for your experiment as outlined in the SOP. Never work in the lab without the necessary safety gear.
3) Maintaining good laboratory housekeeping practices and designated waste disposal procedures
A cluttered lab with spilled chemicals and improperly disposed waste is a recipe for disaster. Here's how good housekeeping prevents fires:
- Clean spills immediately: Don't let flammable liquids sit on the benchtop. Clean up spills promptly using appropriate spill kits.
- Keep work areas organized: Clutter can obstruct exits and make it difficult to move around safely in the event of a fire.
- Dispose of waste properly: Flammable waste must be disposed of in designated containers according to safety regulations.
Maintain a clean and organized workspace. Follow the designated procedures for disposing of chemical waste.
4) Regular safety training and refresher courses for laboratory personnel
Knowledge is power, especially when it comes to lab safety. Regular safety training helps you stay up-to-date on best practices and recognize potential hazards. Here's why safety training is essential for fire prevention:
- Understanding fire hazards: Training teaches you how to identify potential fire risks in the lab and how to mitigate them.
- Safe handling techniques: Refresher courses ensure you remember the proper ways to handle flammable liquids, operate equipment and respond to emergencies.
- Fire extinguisher training: Knowing how to use a fire extinguisher can be critical in containing a small fire before it escalates.
Participate in all mandatory safety training programs and refresher courses offered by your lab.
By following these simple measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of fire in your laboratory. Remember, fire safety is everyone's responsibility. By working together and following these guidelines, we can create a safer and more productive work environment for all.
Conclusion
Preventing laboratory fires is crucial for safety. Always store chemicals properly and handle them with care. Regularly inspect equipment to ensure it is in good working condition.
Use protective gear and follow safety protocols. Educate your team on emergency procedures and fire extinguisher use. Stay vigilant and maintain a clean work environment. By taking these steps, you can significantly reduce the risk of fires in your lab.
Remember, safety is everyone's responsibility. Stay informed, stay prepared, and keep your lab a safe place for scientific discovery and innovation.
Latest Blogs